Do you want to grab a job in the field of AI ML? Check out the top 25 AI ML interview questions with answers categorised separately for beginners, intermediates and advanced learners.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have become the most important aspect, not only in the tech field but in every industry and organisation. AI ML are reshaping industries in 2025 and providing a lot of career opportunities for freshers and professionals.
If you are preparing for interviews, it is beneficial if you prepare the frequently asked AI ML interview questions thoroughly, as it will help you to understand the interview pattern and the difficulty of the questions asked.
In this blog, we will discuss the top 25 AI ML interview questions, ranging from basic to an advanced level, including some of the tips to answer them effectively and ensure your selection in your dream company.
Table of Contents
Why Should You Prepare For AI ML Interview Questions?
The job market is currently filled with AI ML jobs due to the increasing demand of tech experts and the shift towards digitalisation. AI ML interview questions don’t just check your coding knowledge, they also test your problem-solving skills, how you apply algorithms and concepts to real-world data, etc.
If you practice the AI ML interview questions frequently, then you will:
- Get a clear understanding of the concepts of AI ML.
- Learn how to apply concepts to real-world data and solve practical problems
- Gain confidence for working on real projects.
Read more: How to prepare for AI ML interview Questions?
How To Prepare for AI ML Interview Questions?
The preparation strategy for interviews depends upon your experience level, skills and knowledge. If you are a fresher preparing for your first interview then you must start with basic AI ML interview questions to first understand the basics and then move towards intermediate-level questions.
If you are a working professional thinking of switching your job and preparing for an interview then you must focus on intermediate to advanced level questions because your resume already shows experience, so no recruiter would ask you a set of basic questions.
Whether you are a fresher or a working professional, you must focus on building your concepts well, understand the basics and then prepare for any interview. This will help you boost your confidence to frame any answer even if you have not prepared for it.
Read more: 7 Best AI ML Courses for Beginners and Undergraduates
Top 50 AI ML Interview Questions With Answers
To help you prepare better for interviews, the top 25 AI ML interview questions are divided into 3 categories: basic, intermediate and advanced. You can start with basic questions and then move towards intermediate and advanced level questions.
Basic-level AI ML Interview Questions 2025
These basic questions will help you to understand the conceptual-based questions which are asked in interviews for AI ML jobs specially from freshers.
Q1. What are some real-life applications of clustering algorithms?
Ans: Clustering is used to group similar data points without prior labels.
Clustering algorithms are used in various real-life applications like:
- Customer segmentation for targeted marketing
- Recommendation systems for personalized suggestions
- Healthcare for grouping patients with similar conditions
- Detecting fraudulent transactions in banking
- Compressing images, organizing documents, etc.
Q2. How to choose an optimal number of clusters?
Ans: You can use any of the three methods to choose an optimal number of clusters:
- Elbow Method: Make a graph of the number of clusters and how well they fit the data. Now, the point where the line bends like an ‘elbow’ is the best number of clusters to choose.
- Silhouette Score: It tells how similar each point is to its own cluster compared to other clusters. The closer the score is to 1, the better the clustering. The best cluster number is the one with the highest average score.
- Gap Statistic: In this method, your clustering is compared with random clusters. If the difference is large, it means that your chosen number is meaningful.
Q3. What is feature engineering and why is it important?
Ans: Feature engineering refers to developing new features by using existing features. For example, converting timestamps into day or month, or combining features like height and weight into BMI.
It is important because well-crafted features lead to a high-performance model.
Q4. What is overfitting in machine learning and how to prevent it?
Ans: Overfitting happens when the model learns patterns as well as the noise present in the data. This results in high performance on the training data but very low performance for the data that the model has not seen earlier.
You can prevent overfitting by various methods like:
- You can use regularization methods like L1 or L2 regularization which is used to penalize the model’s weights to avoid overfitting.
- It can also be prevented by applying cross-validation or collecting more training data.
Q5. What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning?
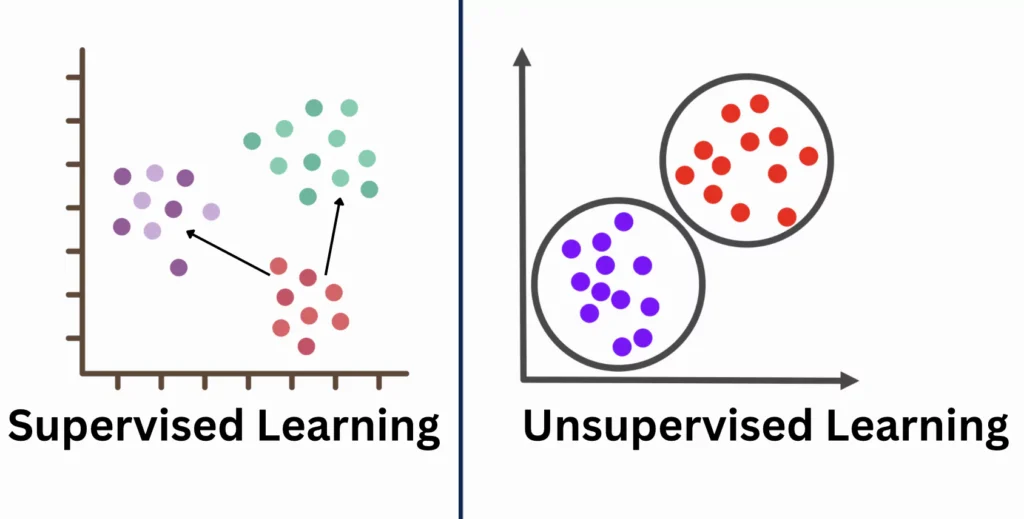
Ans: Supervised learning is the one in which models learn from labeled datasets, where input-output pairs are provided. For example, predicting whether or not the loan will be approved, whereas unsupervised learning is the one that works on unlabeled data to find hidden structures or clusters. For example, customer segmentation.
Read More: 7 Best AI ML Courses For Beginners And Undergraduates 2025
Q6. What is the difference between KNN and K-Means?
Ans: K-means and KNN are one of the most popular AI ML Interview questions targeted during an AI ML job roles. KNN refers to K-Nearest Neighbors, it is a supervised algorithm that is used for classification or regression. It predicts a label based on neighbors.
K-Means is an unsupervised algorithm used for clustering, it groups data into K clusters based on similarities.
Q7. What is the difference between classification and regression?
Ans: Classification and regression are different from each other as classification predicts categorical outcomes like whether a particular thing is spam or not, whereas regression predicts continuous values like predicting stock values.
👉 Both of these fall under the category of supervised learning but are different if we compare on the basis of the type of output.
Q8. What are training, validation and testing datasets?
Ans: Training, validation, and testing datasets are completely different from each other and hence a popular AI ML interview questions.
Training dataset: It is used to fit the model.
Validation dataset: It helps tune hyperparameters and avoid overfitting.
Testing datasets: It is the final dataset to evaluate the performance on unseen data.
Q9. What are the advantages of Naïve Bayes?
Ans: Naïve Bayes is simple, efficient and works well with small datasets. It is particularly effective for text classification and spam filtering, Although there is an assumption of feature independence, it gives surprising results.
Q10. What is ensemble learning?
Ans: Ensemble learning combines multiple models to produce better performance than a single model. For example, bagging, boosting and stacking. These methods reduce bias, variance and improve overall prediction accuracy.
Read More: AICTE Virtual Internship For Freshers 2025: Apply Now!
Q11. What is reinforcement learning?
Ans: Reinforcement learning (RL) is a type of machine learning where an agent learns b y interacting with an environment and receives rewards or penalties for its actions. For example, Training a robot to walk or teaching AI to play chess. The goal is to maximize rewards over time.
Q12. What is the difference between AI, ML and Deep Learning?
Ans: AI, ML and Deep Learning are the three different concepts which you often hear together because of the industry-relevance.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial Intelligence is a broader concept of making machines ‘smart’.
Machine Learning (ML): Machine Learning is a part of Artificial Intelligence where systems learn patterns from data.
Deep Learning: Deep Learning is a part of Machine Learning which uses neural networks with many layers to process complex data like images and speech.
Q13. What is the difference between parametric and non-parametric models?
Ans: Parametric models have a fixed number of parameters, for example, linear regression, logistic regression. They are fast but might not capture complex patterns whereas the number of parameters in non-parametric models grow with data, for example, KNN, Decision Trees. They adapt the data better but can be expensive.
Q14. What is a confusion matrix?
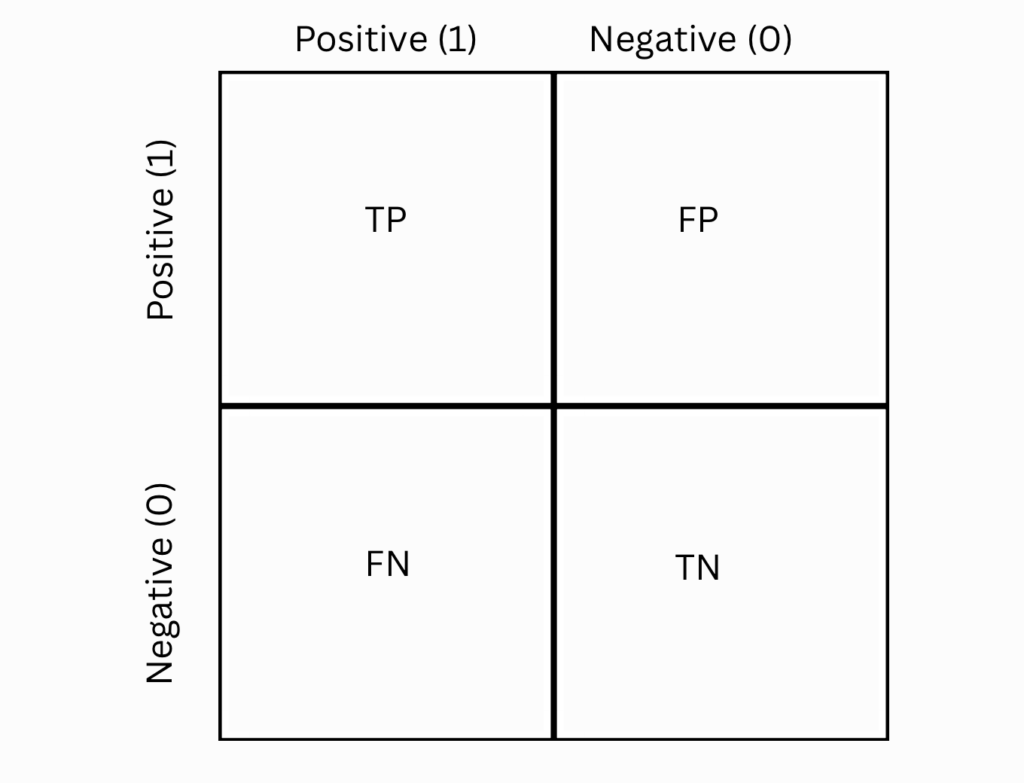
Ans: A confusion matrix is a table that summarizes the classification of a model. In a confusion matrix, you get four types of output (in case of binary classification problem) which are TP, TN, FP and FN.
TP: True Positives
TN: True Negatives
FP: False Positives
FN: False Negatives
It helps you to calculate matrica like accuracy, precision, recall and F1-score.
Q15. What is regularization in ML?
Ans: Regularization is a technique that is used to avoid overfitting by adding a penalty to large coefficients in models.
L1 Regularization (Lasso): It shrinks some weights to zero
L2 Regularization (Ridge): It shrinks weights but keeps all the features.
Read More: ChatGPT 5: Breakthrough or Breakdown?
Intermediate-level AI ML Interview Questions
Now, let’s move towards intermediate-level questions to boost your interview preparation. Prepare these questions well and take a step forward towards your dream job.
Q16. What is dimensionality reduction and why is it needed?
Ans: Dimensionality reduction reduces the number of features but it keeps the important information intact. It is needed because high-dimensional data can cause overfitting, increase computation and degrade performance. Some of the techniques of dimensionality reduction are: PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and t-SNE.
Q17. What is the difference between Random Forest and Gradient Boosting?
Ans: Random Forest reduces variance whereas Gradient Boosting reduces bias. Random forest uses bagging and builds multiple independent trees and averages the results to reduce variance.
Gradient Boosting uses boosting, builds trees sequentially, where each new tree reduces the errors of the previous tree which leads to the reduction of bias.
Q18. What are the key components of a Decision Tree?
Ans: A decision tree has four main components: root node, decision nodes, branches and leaf nodes.
- Root node: It represents the entire dataset.
- Decision nodes: It points where data is split based on conditions.
- Branches: These are the paths representing outcomes of decisions.
- Leaf nodes: Leaf nodes are the final predictions. These are actually the outcomes.
Q19. What is the bias-variance tradeoff?
Ans: Bias is the error which occurs due to oversimplified assumptions. It is also known as underfitting.
Variance is the error which occurs due to excessive sensitivity to training data. It is also known as overfitting. A good model has a balance between both low bias and low variance.
Q20. What is cross-validation and why is it important?
Ans: Cross-validation is used to split data into multiple folds and evaluate it on the basis of various subsets. The most common cross-validation k-fold cross-validation which makes sure that the model is stable, it reduces the risk for overfitting and provides a more reliable performance.
Q21. How will you handle missing or inconsistent data?
Ans: You can handle missing or inconsistent data by the following ways:
- By removing rows or columns which has too many missing values
- By using mean, median and mode
- By using advanced methods like KNN or regression
You must handle missing or inconsistent data properly to avoid bias and errors.
Q22. What are hyperparameters and how can you find them?
Ans: Hyperparameters are like the settings of a machine learning model which you choose before the training. For example, in a decision tree, the depth of the tree is a hyperparameter. If you want to find the best hyperparameter, you can try various methods like:
- Grid Search: It tests all the possible combinations.
- Random Search: As the name suggests, it tests random combinations but it is faster than grid search.
A good hyperparameter makes a model more accurate and reliable.
Q23. How will you measure model accuracy?
Ans: The method to check the model accuracy depends on the type of problem. For different problems, different approaches are required to correctly measure the model accuracy.
- For classification (yes/no or categories): First of all, you will have to understand what accuracy, precision, recall and F1-Score are.
- Accuracy: It means that how many predictions are correct out of all the predictions.
- Precision: It tells how many were actually correct out of the ones you said were correct.
- Recall: It tells that out of the ‘real’ correct ones, how many you found out.
- F1-Score: It is a balance of precision and recall.
- For regression (numbers or continuous values): If the model predicts numbers, then we use methods like MSE, RMSE and R2
- MSE (Mean Squared Error): It is the average of how far the predictions are from real values.
- RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error): It is the same as MSE but easier to read.
- R2 (R-Squared): It shows how the model explains the data. 1 means perfect.
Q24. What is the difference between one hot encoding and ordinal encoding?
Ans: One hot encoding and ordinal encoding are different methods to convert categorical features into numbers. In one hot encoding, a separate column is created for each category and gives a number 0 or 1 according to the category that row has.
For example, you have a feature ‘color’ with categories: Red, Blue and Green. In one hot encoding, you will see the results as shown in the below table.
For red:
| Red | 1 |
| Blue | 0 |
| Green | 0 |
For blue:
| Red | 0 |
| Blue | 1 |
| Green | 0 |
In ordinal coding, the categories are replaced with numbers from 0 to n-1 based on the order, where n is the number of unique categories present.
Ordinal encoding is used only when there is a meaningful order between categories so that they can be organised in an order or given a rank.
Q25. What challenges do you face while deploying ML models?
Ans: When you deploy ML models, you might face various challenges like:
Data pipeline issues: It means to make sure that the correct data is flowing across the model.
Scalability: The model must work well even if there are millions of users using it at the same time.
Latency: Latency refers to speed. The predictions should be done fast. A fraud detection system can’t take minutes to respond and detect the error.
Model Drift: The model must be updated on a regular basis. Otherwise, the model may become less accurate if it is not updated.
Fairness and Bias: You have to make sure that the models are not giving unfair and biased results.
Q26. What is bagging in ensemble methods?
Ans: Bagging or Bootstrap Aggregating is an ensemble technique where various models are trained on random subsets of data and their predictions are averaged.
For example, random forest uses bagging with decision trees. It helps reduce variance and overfitting.
Q27. What is boosting in ML?
Ans: Boosting is an ensemble technique where models arew trained sequentially and each new model tries to correct the errors of the previous one.
Some of the popular boosting algorithms are: AdaBoost, XGBoost, LightGBM and CatBoost.
Q28. What is feature selection and why is it important?
Ans: Feature selection is the process of choosing the most important features for training a model. It is important because it reduces overfitting, improves accuracy and decreases training time.
Different methods used are: filter methods (correlation), wrapper methods (forward selection), embedded methods (Lasso).
Q29. What is the difference between batch learning and online learning?
Ans: In batch learning, the model is trained on the entire dataset all at once. It is suitable for small to medium datasets whereas in online learning, the model is trained alongside as the new data arise. It is useful for streaming or large-scale data.
Q30. What is gradient descent?
Ans: A gradient descent is an optimization algorithm used to minimize a cost or loss function by updating model parameters in the direction of negative gradient (also known as steepest descent).
Some of the variants are: Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), Mini-batch Gradient Descent.
Q31. What is PCA and how does it work?
Ans: PCA refers to Principal Component Analysis. It is a technique used for dimensionality reduction in which you trade off some information or patterns of data at the cost of reducing its size significantly.
PCA works by:
- Finding directions (principal components) where the variance in data is maximum.
- Projecting data onto these components.
This helps to reduce dimensions while preserving the information. By using this algorithm, you can compress images, visualise high-dimensional data as well as you can make data visualization easy.
Q32. What is data leakage in ML?
Ans: Data Leakage is a situation when there is a high correlation between the target variable and the input features. It happens when information from outside the training dataset is used to build the model. Data leakage results in optimistic results but poor real-world performance.
For example, using future data to train a time-series model.
Q33. What are under-sampling and over-sampling in ML?
Ans: Under-sampling and over-sampling are both used to handle class imbalance problems.
- Under-sampling: It involves decreasing the samples in the majority class by selecting some random number of points that are equal to the number of data points in the minority class so that the distribution becomes balanced.
- Over-sampling: It involves increasing the samples in the minority class by randomly selecting some points from the minority class and adding them to the dataset, and repeating this process until the datasets gets balanced for each class.
Q34. What is A/B testing in ML?
Ans: A/B testing is an experimental model which is used to compare two versions of a model, algorithm, system or approach (Version A and B) to find out which one performs better. It helps in practical decision-making instead of relying on assumptions.
Q35. What is model interpretability and why is it important?
Ans: Model interpretability means understanding how a model makes predictions. It is important because of multiple reasons, such as:
- It helps to build with stakeholders
- It helps in debugging model errors
- It helps to ensure transparency and fairness
Some of the techniques used for model interpretability are: SHAP values, LIME, feature importance, etc.
Advanced-level AI ML Interview Questions
Now, let’s move towards an advanced set of questions. These are some of the frequently asked questions and there are high chances of these questions repeating in your interviews for AI ML jobs.
Q36. How will you monitor deployed ML models?
Ans: You can track the performance of an ML model which has been deployed by using performance tracking metrics like accuracy, precision, recall.
You must monitor input data for checking model drifts. Setting up alert systems and scheduling retraining (updates) when performance goes down also helps to keep a track of ML models. MLflow and Kubeflow are two most used tools to monitor deployed ML Models.
Q37. What is the curse of dimensionality?
Ans: When more and more features (columns) are added to a dataset, it can lead to a few problems which are known as the curse of dimensionality.
- Data spreads out, the data points are way too far to be judged.
- Algorithm struggles arise. Methods like k-NN or clustering do not work.
- Due to too many features, the model may overfit. It might memorize the data instead of learning the patterns.
Q38. What is the difference between generative and discriminative models?
Ans: Generative models understand inputs and outputs. It can even create new data like fake images, text, etc. For example, Naïve Bayes, GANs. Discriminative models just predict the output based on the input you provide. It cannot create any new data. For example, Logistic Regression, SVM.
Q39. How will you explain ML results to non-tech stakeholders?
Ans: To explain ML results to non-tech stakeholders, you can use visuals like charts, graphs etc. Make sure to avoid technical jargon as it might be overwhelming for non-tech people to understand what you are saying. Use simple language to explain your point.
For example, instead of using the term ‘precision’ to explain ‘precision increased’, you can simply explain how it reduces false positives and saves cost.
Q40. What is the use of CNN?
Ans: CNN refers to Convolutional Neural Network. These are specialized deep learning models used for image-related tasks like object detection, facial recognition and medical imaging. Convolutional layers, pooling and fully connected layers are used to extract spatial features.
Q41. What are RNNs? Why are they used?
Ans: RNNs are Recurrent Neural Networks. These are designed for sequential data where the output depends on previous inputs. It is mainly used in language modeling, text generation, speech recognition, time-series forecasting.
Q42. What is transfer learning?
Ans: Transfer learning means reusing a pre-trained model like ResNet, BERT on a new but related task. It saves training time, requires less data and improves performance.
Q43. What is the vanishing gradient problem in deep learning? How can you solve it?
Ans: The vanishing gradient problem happens during backpropagation when gradients become extremely small as they move backward through many layers. This makes early layers learn very slowly which leads to poor training.
- It happens due to activation functions like sigmoid or tanh that squash values into a small range (0-1) which causes repeated multiplication of small numbers.
- It slows down or completely stops the training of deep networks.
- To solve the problem of vanishing gradient, you can use ReLU activation, batch normalization, residual connections (ResNets) or specialized architecture like LSTM/GRU for sequential data.
Q44. What are Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)?
Ans: Generative Adversarial Networks, commonly abbreviated as GANs are used for generating realistic images, videos and even synthetic data. It consist of two networks:
- Generator: It creates fake data.
- Discriminator: It tries to distinguish fake data from real data.
Q45. What is attention mechanism in deep learning?
Ans: The attention mechanism in deep learning allws models to focus on important parts of the input while making predictions. It is used in transformers and models like BERT, GPT, etc.
For example, In NLP, attention mechanism helps a translation model focus on relevant words from the source sentence.
Q46. What is reinforcement learning’s exploration vs exploitation dilemma?
Ans: In reinforcement learning, an agent must balance exploration (trying new actions to discover potentially better rewards) and exploitation (choosing the best action to maximize immediate rewards).
Excess of exploration wastes time and excess of exploitation may result in missing out of better options.
Methods like Thompson Sampling can help in maintaining this balance.
Q47. What is MLOps?
Ans: MLOps or Machine Learning Operations is the practice of deploying, monitoring and maintaining ML models in production efficiently. It combines ML with DevOps practices to handle the full lifecycle from data collection to monitoring deployed models.
Q48. What is the difference between offline and online evaluation of ML models?
Ans: Both offline and online evaluation models are used to test ML models. Offline evaluation is used to test models using historical test datasets before deployment of the model. Online evaluation is used to test models in production (real-world data) using methods like A/B testing or shadow deployment.
Q49. What are autoencoders and where are they used?
Ans: Autoencoders are neural networks that learn to compress data into a smaller form (encoding) and then rebuild it back (decoding). It is used for anomaly detection, denoising images and dimensionality reduction.
Q50. Describe a challenging ML project you worked on.
Ans: This is one of the most asked questions in interviews for AI ML jobs especially if you have prior experience.
You can structure you answer for this question in the following manner:
Problem: The problem you faced in the project
Approach: Tell about the techniques you used or models applied
Challenges: Discuss about the challenges you faced like data imbalance, noise, inconsistent data, etc.
Outcome: Tell how you overcame this problem and what were the results that you achieved.
Sample Answer: In one of my projects, I worked on predicting customer churn. It was the most challenging project I’ve come across because of the data imbalance.
However, I managed to balance the data using SMOTE. I tested different models and finally used Random Forest with cross-validation.
In the end, it helped the company to identify the customers who were most likely to leave and the model gave good accuracy.
Upskill With Pregrad🔥
If you want to make your career in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning and secure one of the best AI ML jobs, then following the right path becomes a necessity in today’s rapidly evolving job market.
Pregrad can help you start from the beginning, and make you job-ready in less than a semester. Your dream job is no longer just a dream. Join Pregrad and take a step forward towards your dream career.
Pregrad is an online learning platform where mentors don’t just fill you up with theoretical knowledge but they focus on building concepts, clearing your basics and providing you a chance to work on real-world projects. You can check out the AI/ML program by Pregrad.
And Pregrad is not just limited to that. You can check out various other programs like Data science and Analytics, Full Stack Development, Cybersecurity, and many more.
At Pregrad, you will get complete 1:1 mentorship with guided live sessions and recordings, career assistance, along with resume building and LinkedIn profiling tips.
AI ML Interview Questions FAQs
Q1. How can I prepare for AI ML interview?
Ans: First of all, you need to clear your basics and you must relevant knowledge about AI ML. If you are a fresher, take help from your seniors, reach out and connect with people on LinkedIn and grasp all the knowledge you get. If you are already a working professional, focus on preparing situation-based questions for interview. You can prepare the top 50 AI ML interview questions mentioned in this blog as these are most frequently asked questions.
Q2. Are these questions enough to appear for AI ML job interview?
Ans: Except the recruiter, nobody can 100% guarantee what will be asked in an interview, but these 50 questions are the most repeated and most important questions that hiring managers often ask in AI ML job interviews. You can prepare these thoroughly and focus on building your concepts so that you can answer any question even without prior preparation.
Q3. Do I need to have projects to crack AI ML interview?
Ans: It is better if you have already worked on a project before as it ensures the hiring company that you have practical experience. Even if you are a fresher, you can work on personal projects and showcase then for your first job interview.
Q4. Is there any programming language which I need to know?
Ans: Yes, if you are trying to get a job in the tech field, then you must be familiar with some of the top programming languages like Python, R, Java, etc. Python is the most important and most used programming language so try to learn and understand it properly.







